Subdomain Finder
What you will see in the report
Subdomain Finder scans the DNS records and supplementary databases to analyze the domain's hierarchy. Our subdomain scanner checks:
- DNS records (NS, MX, TXT, AXFR)
- DNS enumeration
- SSL certificates
- HTML links
- Search engine results
- Reverse DNS for target IP addresses
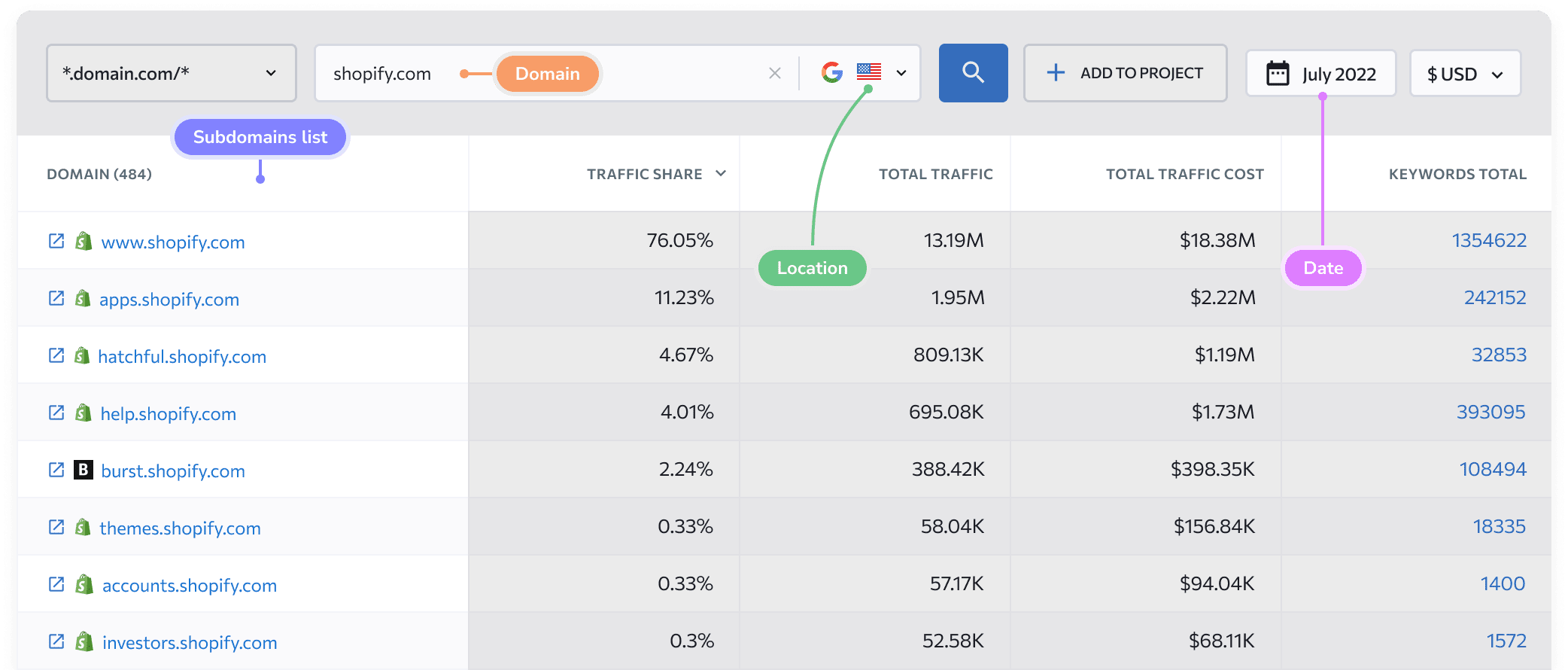
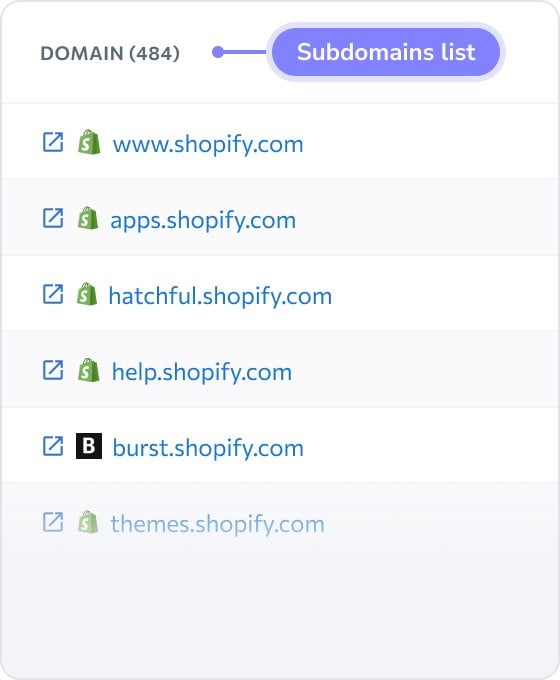
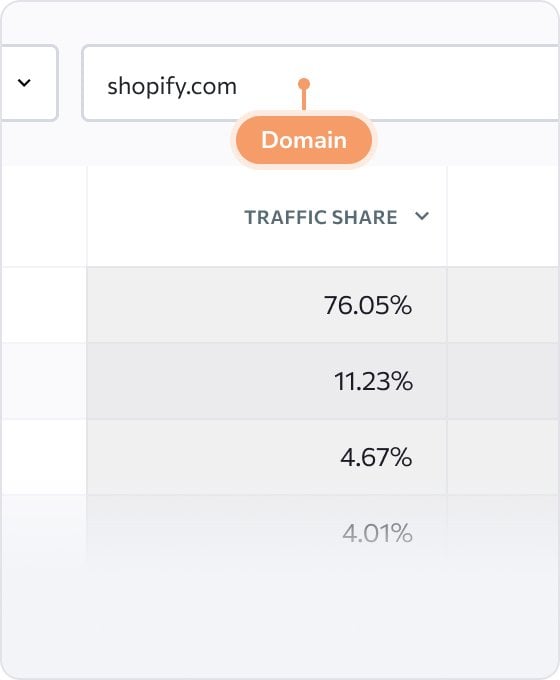
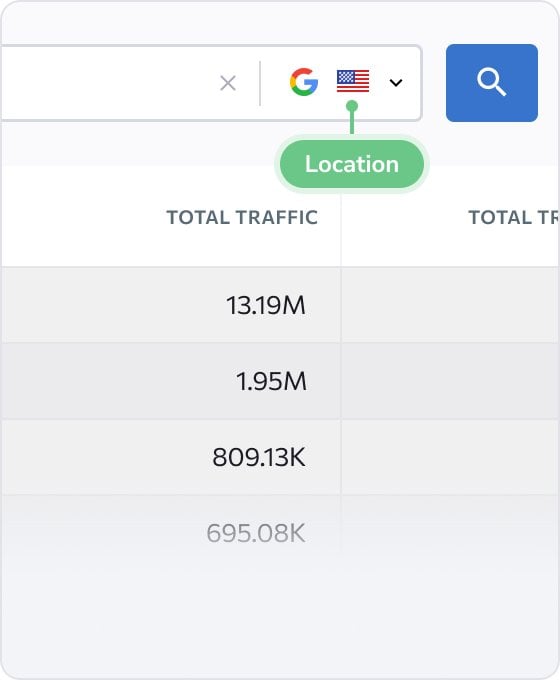
Subdomain Finder is straightforward to use. To start, enter the target domain address and click Scan. The tool will take you to Subdomains section of SE Ranking’s Competitive Research, which reveals comprehensive, up-to-date data on every found subdomain—access data on traffic volume, share, and cost, along with the number of keywords. Filter subdomains by any metrics and access the detailed keywords report by clicking on the number of keywords. Finally, click the Export button to download the report in the .csv or .xsl format.
Subdomain scanner ensures the highest accuracy of results. It aggregates relevant information from search engines and supplementary databases and sends additional requests to domain service providers to get the most complete and up-to-date results. The scanner is secure; we don’t save or publish any information about checked domains and their subdomains.
FAQ
There are several ways to find subdomains:
- Manually, by using the site:* operator in Google
- By checking DNS records using the nslookup command
- By using our online subdomain scanner or similar tools
You can find DNS records using the nslookup command in the command line. It shows all DNS records for a given domain, including a list of subdomains. The command works for Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems.
The subdomain is displayed as a separate search result. Most search engines, including Google, consider subdomains as separate sites—they crawl, index, and rank them independently from the main site. Therefore, optimising the main domain and its subdomains is equally essential.
Yes, subdomains can be hidden. There are several ways to do this:
- Hide it from crawlers using the disallow directive in the robots.txt file
- Hide it from indexing—use the noindex or none directive in the robots meta tag in the HTML code of the page
- Set the X-Robots-Tag HTTP headers to noindex or none on the subdomain server
It is impossible to hide a subdomain from scanning completely. Subdomain checkers use publicly available DNS registers to find information. But even if the scanner has detected a subdomain, it does not necessarily mean that the page is publicly accessible—its content can be hidden.
Subdomain takeover happens when a subdomain points to a non-active external service, but the CNAME used for that service is still in the DNS records. Hackers can set up a virtual host for the subdomain and gain control over it.
SEO-wise, subdomains are separate sites. They are associated with the domain name but not with the site itself. Subdomains are used for different tasks:
- site localization for various regions
- separating categories of goods, services, or information
- publication of user-generated content
- separate render of the site application
- testing new site elements
Technically, yes. You can find it among other subdomains in the search results, but it often redirects to the main domain. When the Internet was first created, the www. prefix was used to distinguish sites that use the Internet protocol. Today, some hosting providers automatically create the WWW subdomain for all sites and set up a redirect.
Theoretically, there is no limit to the number of subdomains, but some DNS servers set restrictions. For example, GoDaddy limits users to 500 subdomains.